Have you ever paused to consider how interconnected your mental and physical health truly are? This question is not merely a philosophical musing; it’s an invitation to explore an intricate relationship that profoundly affects every aspect of your life. In today’s fast-paced world, understanding the interplay between mental and physical health has never been more pertinent.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Table of Contents
Overview
The interplay between mental and physical health is a dynamic relationship where changes in one can significantly affect the other. This holistic approach underscores the importance of treating the mind and body as interconnected systems. By examining this relationship, you can better understand how to achieve overall well-being.
Thesis Statement
In this article, we will delve into the intricate link between mental and physical health, offering a comprehensive understanding of how each influences the other. This examination is crucial for recognizing the importance of a holistic approach to health and well-being.
Historical Context
Historically, mental and physical health were often considered separate domains. Ancient Greek physician Hippocrates, often called the “Father of Medicine,” approached health through a holistic lens, emphasizing the balance of bodily fluids and lifestyle integration. However, over time, Western medicine primarily focused on physical symptoms, often sidelining mental health.
The Evolution of Mental Health Appreciation
With the advent of psychology and psychiatry in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the medical community began acknowledging mental health as a critical component of overall health. Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theories, though controversial, spurred interest and research into the mind’s complexities.
Current Trends
Today, the appreciation for the interconnection between mental and physical health has gained significant traction. Modern healthcare increasingly adopts integrated care models, which blend mental and physical health services. This paradigm shift is evident in the growing fields of psychoneuroimmunology and behavioral medicine, which study how psychological factors affect physical health and vice versa.
Key Concepts and Definitions
To fully appreciate this intricate relationship, it’s essential to understand some key terms:
Mental Health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how you think, feel, and act, and thus plays a significant role in how you handle stress, relate to others, and make choices.
Physical Health
Physical health pertains to the well-being of the body and its organs. It includes practices that maintain bodily functions, such as exercise, nutrition, and sleep.
Psychoneuroimmunology
This field examines the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. It underscores how stress and emotional states can impair immune function, leading to various illnesses.
Behavioral Medicine
Behavioral medicine integrates behavioral and biomedical knowledge to prevent, diagnose, and treat health issues. It fosters the understanding that lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, greatly influence one’s overall health.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Breaking It Down: The Mind-Body Connection
The Physiological Pathway
There are physiological pathways through which mental and physical health influence each other. For instance, chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, impairing immune function and increasing the risk of chronic diseases like hypertension and diabetes.
Psychological Well-being and Physical Health
Mental well-being significantly impacts physical health outcomes. For example, depression has been linked to heart disease, while anxiety can exacerbate conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle choices often stem from poor mental health. Individuals struggling with depression may neglect physical activity, leading to weight gain and associated physical health issues. Conversely, regular exercise can elevate mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Example 1: Depression and Heart Disease
Studies have shown that individuals with depression are at a higher risk of developing heart disease. The American Heart Association recognizes depression as a risk factor for poor prognosis among patients with coronary artery disease. This relationship underscores the need for integrated care addressing both mental and physical health components.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Example 2: Anxiety and Gastrointestinal Disorders
Anxiety and gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), often coexist. Anxiety can exacerbate IBS symptoms, leading to a vicious cycle of discomfort and mental stress. Treatment strategies that address both anxiety and gastrointestinal health tend to be more effective.
Comparing Different Points of View
When comparing different perspectives on the mind-body connection, several schools of thought emerge:
| Perspective | Key Idea | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Holistic Health | Integrates mental, physical, emotional, and social health | Mindfulness practices |
| Biomedical | Focuses on physical symptoms and treatments | Medication for hypertension |
| Psychosomatic Medicine | Considers the psychological impact on physical ailments | Cognitive-behavioral therapy for chronic pain |
| Behavioral Medicine | Merges behavioral and biomedical approaches | Lifestyle interventions |
Impact Assessment
Analyzing these perspectives reveals the multifaceted nature of health. Holistic approaches and behavioral medicine emphasize the unity of mind and body, fostering more comprehensive and effective treatment strategies. Meanwhile, the biomedical approach may sometimes neglect the mental health aspect, potentially leading to incomplete care.
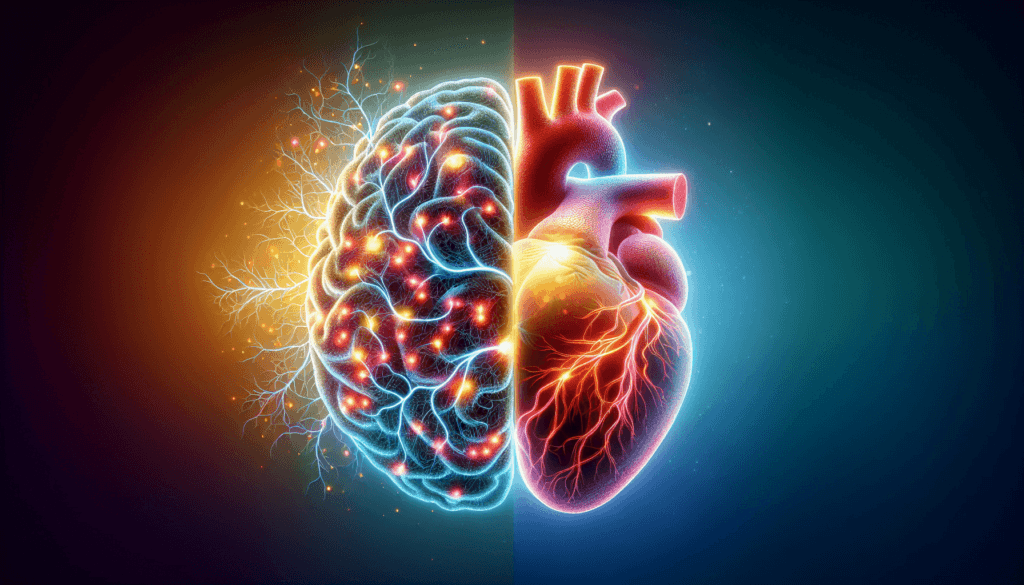
Future Directions and Implications
Predictions
The future will likely see an even greater emphasis on the integration of mental and physical health. Telehealth platforms and wearable health technology will play key roles in monitoring both mental and physical well-being simultaneously. Collaborative care models will become more common, where mental health professionals, primary care practitioners, and specialists work together to provide comprehensive care.
Implications for Society
This integrated approach will have far-reaching implications for healthcare, potentially reducing the burden of chronic diseases and improving quality of life. Insurance companies may also incentivize holistic wellness programs, recognizing the cost-efficiency of preventive care.
To conclude, the interplay between mental and physical health is an intricate and dynamic relationship that significantly influences your overall well-being. Historical changes, current trends, and future directions all point toward the increasing integration of these two domains, highlighting the necessity of a holistic approach to health. What are your thoughts on the importance of integrating mental and physical health care?
For further insight, you might find it beneficial to read other articles on mental health’s impact on chronic illnesses or the advantages of integrated care models.

